Linear adjustment mechanism
// Medical Technology
Ref-Nr: 16333
Abstract
This technology offers an innovative linear adjustment mechanism, which has increased dynamics and modularity in a smaller space requirement compared to the prior art.background
In minimally invasive diagnosis and therapy, robotic instruments and manipulators have been established as a part of assistance systems. Those allow surgeons to apply significantly more complex surgical techniques intracorporeally. An actuator unit arranged outside the patient’s body provides the necessary manipulation forces. For this, the spatial distance between the instrument and / or manipulator on the one side and the actuator unit on the other side should be bridged with adjustable means. In previous systems e. g. cable tensions are used.
Innovation / Solution
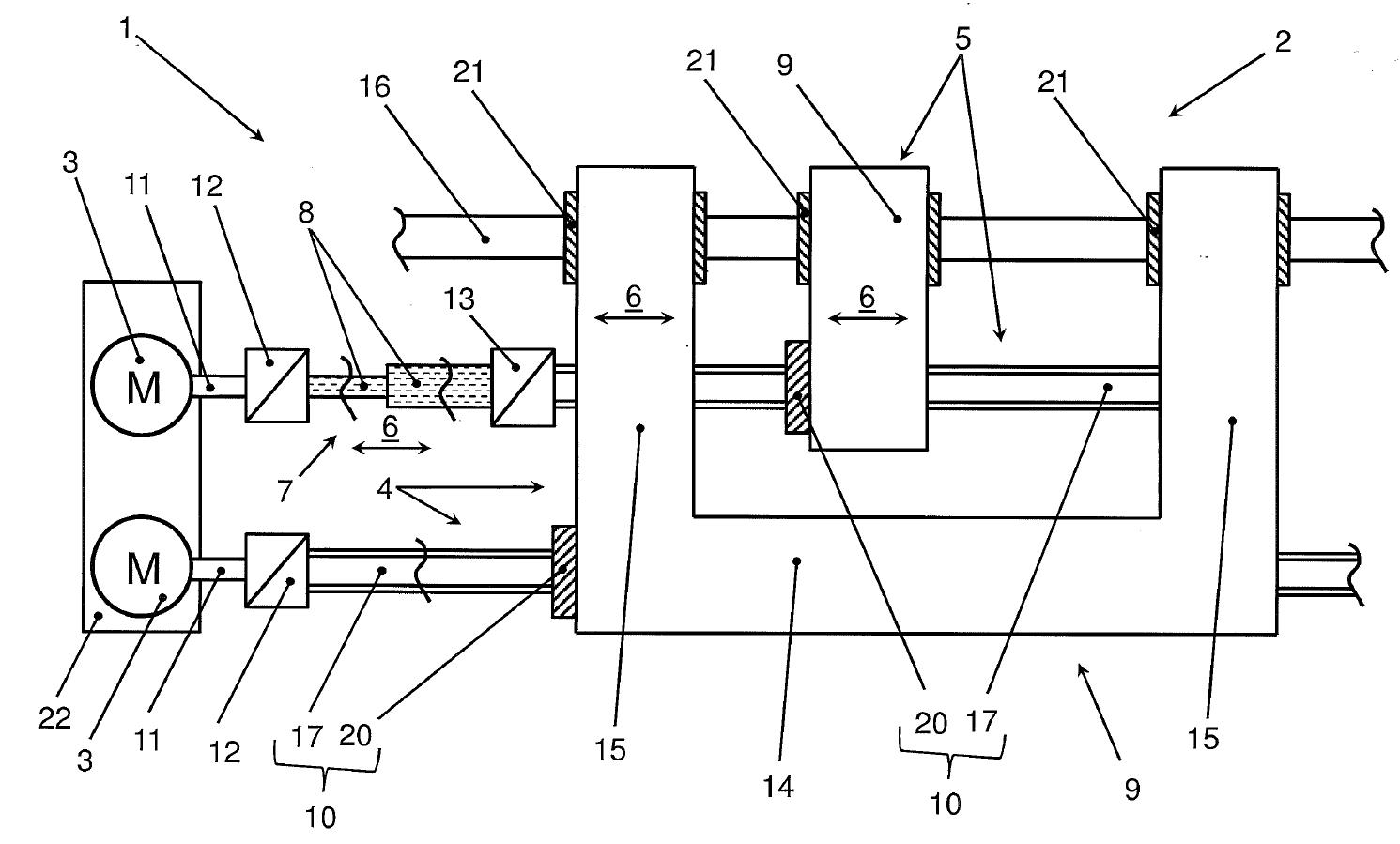
The invention represents a linear adjustment mechanism, which possesses increased dynamics and a higher modularity while requiring less space compared to the prior art. The motor-driven linear adjustment mechanism (see Fig. 1) has at least one movable push-pull axis module (2) arranged on the linear adjustment mechanism (1) and at least two actuators (3) per push axis module and at least two linear units (4, 5) for the push axis module. With the arrangement according to the invention, a compensation of the occurring differences in length of the drive shafts (11) can be achieved and thus a bracing of segments of the manipulator arm can be prevented. Thus, the positioning units, despite mechanical coupling and differences in length, can be driven independently and with stationary motors. To realize multiple degrees of freedom, the modules can be arranged, for example, concentrically.Benefits
Compact design: very small center distances of the motors
Drives do not have to be moved and can be completely decoupled from the mechanism (sterile reconditioning)
Due to the weight reduction, the energy requirement decreases
fields of application
medical operations, minimally invasive surgery, robot assisted surgery, flexible manipulator arms, industrial positioning tasks, continuum robotics, soft roboticsYou can close this window. You can find your search results in the previous window