Method for improving the quality of a person’s hearing, cochlear implant as well as cochlear implant system
Abstract
According to the invention, a method for im-proving the hearing quality of a person with hearing impairment by means of a cochlear implant is proposed. The cochlear implant has an external unit and is effectively connected to the hearing apparatus of the person by means of electrodes.background
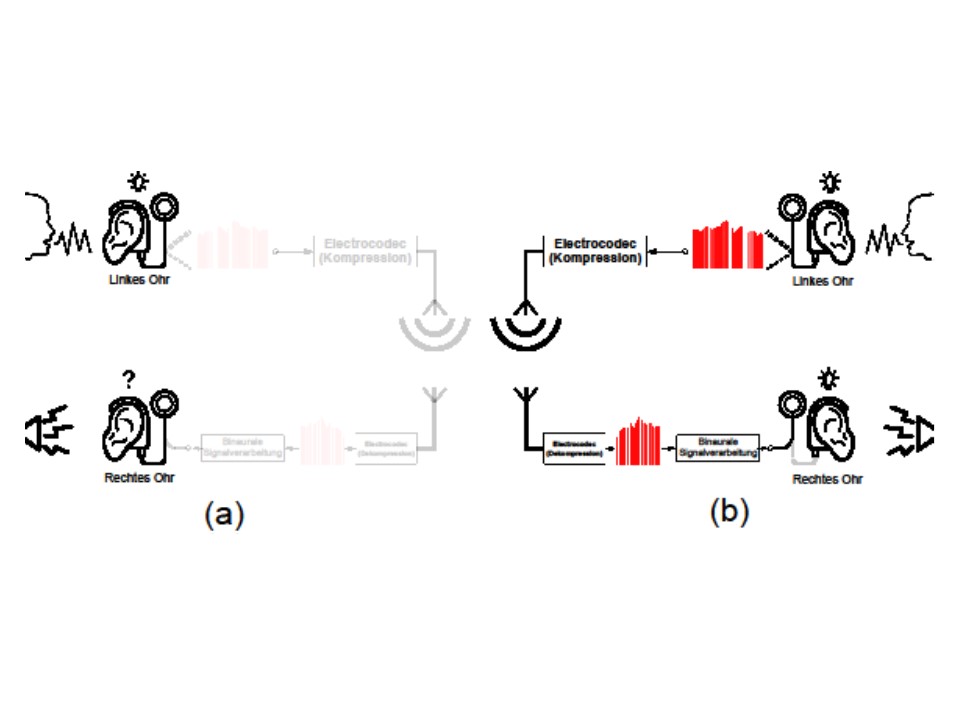
Wireless communication of cochlear implant signal processors with external devices is widely used today. For example, external microphones can be placed right next to a teacher so that the teacher’s voice is transmitted wirelessly via the external microphone to one or more signal processors. This can significantly improve the speech understanding of CI-users in difficult situations. Likewise, binaural signal processing strategies require wireless communication of audio data. These combine information from two CI signal processors or CI microphones to improve the overall speech understanding or localization of a CI-wearer.
In any case, the necessary wireless communication is energy-intensive. Since CIs draw their energy from batteries, this is severely limited and the audio data to be transmitted is usually compressed before it is transmitted wirelessly. It is also essential that the compression takes place with low latency so that there is no large time delay between receiving and sending the audio data.
The technology presented here includes a novel approach to compressing and transmitting audio data for wireless communication with CI signal processors.
Conventional audio compression methods typically compress the audio signal recorded by a microphone and thereby achieve unfavorable bit rate and latency ratios. This generally affects either the quality of the audio signals, the battery life or the perception of the CI-user due to impaired signal processing as a result of high latencies.
Our approach is to compress the excitation patterns, the sequence of current values that a CI signal processor generates from the audio signals. After compression, these can be transmitted wirelessly in an energy-saving manner. For this purpose, a special compression algorithm was developed, which compresses the excitation patterns, which were generated e.g. with the Advanced Combinational Encoder tone coding strategy, latency-free and with a low bit rate.
Laboratory tests have shown the superiority of our method compared to conventional audio compression.
With the presented technology, especially audio data from external microphones or other signal processors can be transmitted wirelessly. More generally, any wireless audio signal transmission can be implemented using the presented specialized compression of CI excitation patterns.
Motivation
Known methods and cochlear implants have the disadvantage that the exchange of data and information between remote devices has to be done with a relatively high data rate and/or latency and thus involves a high turnover of electrical energy or signal processing algorithms may be affected and the sensation of the CI-user may be impaired.Innovation / Solution
Instead of compressing the audio signal captured by the microphones of the CI, the CI stimulation patterns are compressed. These are created by the sound coding strategy of the CI. Examples of sound coding strategies include Continuous Interleaved Sampling (CIS), Ad-vanced Combinational Encoder (ACE) and the psychoacoustic ACE.Benefits
fields of application
Binaural signal processing for cochlear implants, wireless streaming of audio information to cochlear implants/signal processors.You can close this window. You can find your search results in the previous window