Optically Controlled Material “OptiContMat”
Abstract
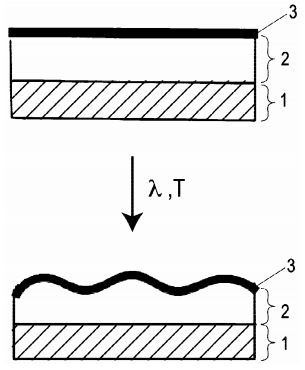
The invention relates to a process for producing a nanostructured layer system which has a substrate, an intermediate layer which is applied to the substrate and contains an aromatic azo compound, in particular an azobenzene-containing low-molecular-weight glass, and a metallic outer layer, the intermediate layer being structured in a light-induced manner.background
The use of films containing azobenzene as information carriers in recordable optical data carriers such as CDs or DVDs is well known. For this purpose, a film containing azobenzene is applied to a transparent carrier and covered by a reflective metal layer, which may contain various metals, including nickel. Laser light of relatively high energy can be used to locally thermally decompose the transparent carrier of the azobenzene-containing film, allowing information to be irreversibly written onto the data carrier. When applied in thin layers, azobenzene-containing films also exhibit light-induced reorientation phenomena.
Innovation / Solution
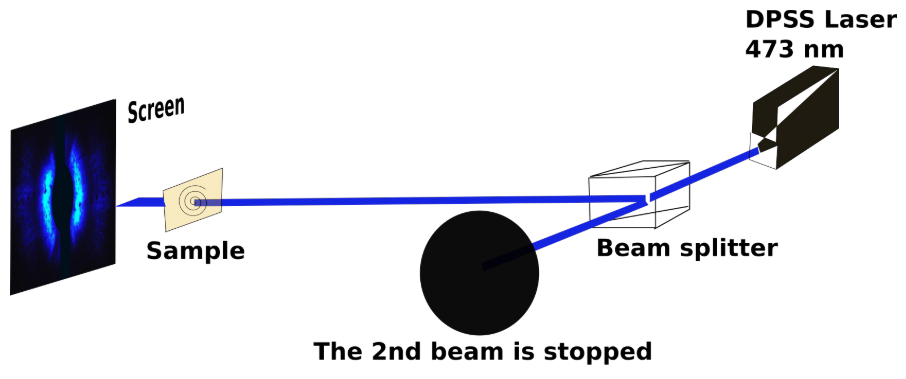
A substrate is provided and an intermediate layer containing an aromatic azo compound is applied. A metallic top layer is then deposited on the intermediate layer and linearly polarised light is irradiated onto the metallic top layer for light-induced structuring of the intermediate layer and the metallic top layer. The nanostructured layer system forms a surface structure that is formed by anisotropic waves extending along a main direction.Benefits
fields of application
The information about the plane of polarisation of the light is directly reflected in the nanostructure of the nanostructured layer system. For this reason, the nanostructured layer system can be used for information storage, for example. Other areas of application are nanoelectronics and microelectronics, optics and the semiconductor industry as well as micromechanical production methods for the medical sector, among others.You can close this window. You can find your search results in the previous window