Fabrication method of textured asymmetric ceramics with high oxygen flux and high stability against carbon dioxide
// Chemistry // Elektrochemie // Energy and Energy Storage Technology // Material Technology // Power Engineering // Surface Technologies // Syntheses and Process Engineering
Ref-Nr: 17344
Abstract
The technology relates to an oxygen-permeable, yet carbon dioxide-resistant, ceramic mixed-conductor membrane and its fabrication.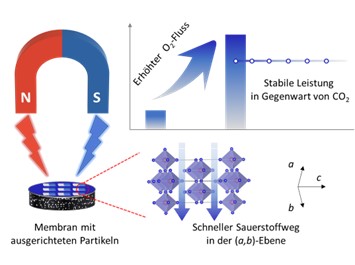
Fig. 1: Nd2NiO4+δ (NNO) particles can be aligned in a magnetic field (< 1 T). A textured asymmetric membrane prepared in this way showed five times higher O2 flux than a conventional membrane. The material also showed excellent CO2 stability, highlighted by an O2 flux of 1.4 mL min-1 cm-2 for 120 h at 950 °C under pure CO2 sweep.
background
Solid oxide fuel cells are high temperature fuel cells and use solid oxide ceramic electrolytes. The solid electrolyte is designed as a thin membrane to transport oxygen ions with low energy. For example, in BSCF ceramics, the presence of carbon dioxide has a strong negative effect on oxygen permeability.
Innovation / Solution
The technology according to the invention relates to an oxide ceramic comprising NNO, said ceramic consisting of a porous support and a dense thin layer. In particular, the grains of the thin layer are aligned by means of a manufacturing step in a magnetic field to significantly increase the oxygen permeation and reach or even exceed the level of BSCF ceramics.Benefits
NNO exhibits excellent chemical stability against carbon dioxide
High chemical and thermal stability at high temperatures (about 750 °C to 950 °C)
fields of application
Applications include use as an electrolyte in solid oxide fuel cells, in the catalytic industry and as a catalytic membrane reactor.You can close this window. You can find your search results in the previous window




